What Organisms Use Lactic Acid Fermentation
Some leaner produce lactic acid from pyruvic acrid. This metabolic process is also seen in the muscle cells of animals. There tin be inadequate oxygen supply for respiration in muscle cells during physical practise. Thus, in anaerobic atmospheric condition, pyruvic acid is reduced to lactic acid. This happens in the presence of the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase. Too, a reducing agent like NADH+H+ is reoxidised to NAD+.
It is a fermentation process where much of the free energy is not released. Here, less than seven per cent of the glucose energy is released. Too, not all of it is trapped as high energy bonds of ATP.
Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration is a kind of cellular respiration that happens in the absence of oxygen. The ii types of anaerobic respiration are – Lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation.
Fermentation
Fermentation usually happens in yeast cells and bacteria. Also, the animate being musculus cells prove lactic acid fermentation in case of inadequate oxygen supply.
In yeast, there is incomplete oxidation of glucose that happens in an anaerobic environment. Hither, pyruvic acid is converted into carbon dioxide and ethanol. Some bacteria produce lactic acid from pyruvic acid past means of lactic acid fermentation.
Steps Involved in Lactic Acrid Fermentation
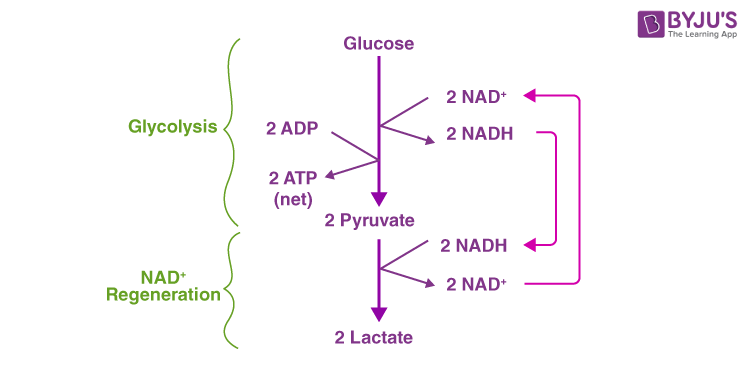
- The glucose or 6-carbon molecule is cleaved down into Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, and and then to 3-Phosphoglyceric acid.
- During this, NAD+ is converted into NADH+H+.
- The 3-Phosphoglyceric acid forms Phosphoenol pyruvic acid, which later forms the Pyruvic acid.
- Cyberspace 2 ATP molecules are formed in this process (glycolysis).
- This Pyruvic acid is reduced to Lactic acid with the assist of reducing agent NADH+H+, which reoxidises to NAD+.
- This process produces two lactate/lactic acrid molecules from two pyruvate/pyruvic acid molecules. This reaction happens in the presence of the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase.
Applications
Lactic acrid fermentation is the best method used for nutrient preservation. Lactobacillus is the almost commercially used bacteria for this process. They are used in the production of pickles, sour beer, fermented fish, yoghurt, etc.
Oftentimes Asked Questions
What is homolactic and heterolactic fermentation?
When one glucose molecule is converted into two molecules of lactate or lactic acrid, it is termed homolactic fermentation. Here, simply lactic acrid is the final byproduct. In heterolactic fermentation, other byproducts like CO2 and ethanol are formed along with lactic acid.
What are facultative and obligate anaerobes?
Facultative anaerobes can produce energy with or without oxygen. Thus, they tin too undergo aerobic respiration. Examples – E.Coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, etc. Obligate anaerobes cannot tolerate oxygen. They are strictly anaerobic. Examples – Clostridium, Actinomyces, etc.
Why do musculus cramps happen?
Inadequate oxygen supply in human muscle cells leads to anaerobic respiration. Thus, lactic acid fermentation takes place to produce free energy molecules. Lactic acid is the byproduct of this procedure. Excessive buildup of lactic acid creates muscle discomfort chosen cramps.
Also Read:
- Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
- Fermentation – Anaerobic Respiration
- Glycolysis
Visit BYJU'S Biology for more exciting topics.
What Organisms Use Lactic Acid Fermentation,
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/lactic-acid-fermentation/
Posted by: beckdiden1961.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Organisms Use Lactic Acid Fermentation"
Post a Comment